Now that you have practiced taking off, landing, and using basic controls in the VEX AIR Flight Simulator, you are ready to learn a new type of movement – pitch. In this lesson, you will explore how pitching the VEX AIR Drone forward and backward allows it to move along the y-axis while keeping the nose, or front of the drone, pointed straight ahead. You will learn how to control pitch with the VEX AIR Drone Controller, and practice flying.
Watch this video to learn more about:
- How to use the right joystick to pitch forward and backward.
- How propeller speed differences create forward and backward motion.
Hover & Discover
Pitch is the control that tilts the drone forward or backward while keeping its nose pointed straight ahead. A drone pitches when the propellers on one end spin faster than the propellers on the opposite end. This change in propeller speed tilts the drone and causes it to move forward or backward along the y-axis.
When the rear propellers spin faster, they push harder against the air, lifting the back of the drone and tilting the nose downward. This causes the drone to move forward across the field.
When the front propellers spin faster, the drone tilts backward and slides in that direction.
Because the drone’s nose remains pointed forward during pitch, the drone can move ahead or retreat without turning.
Mission: Fly Through a Ring
Understanding Your Drone
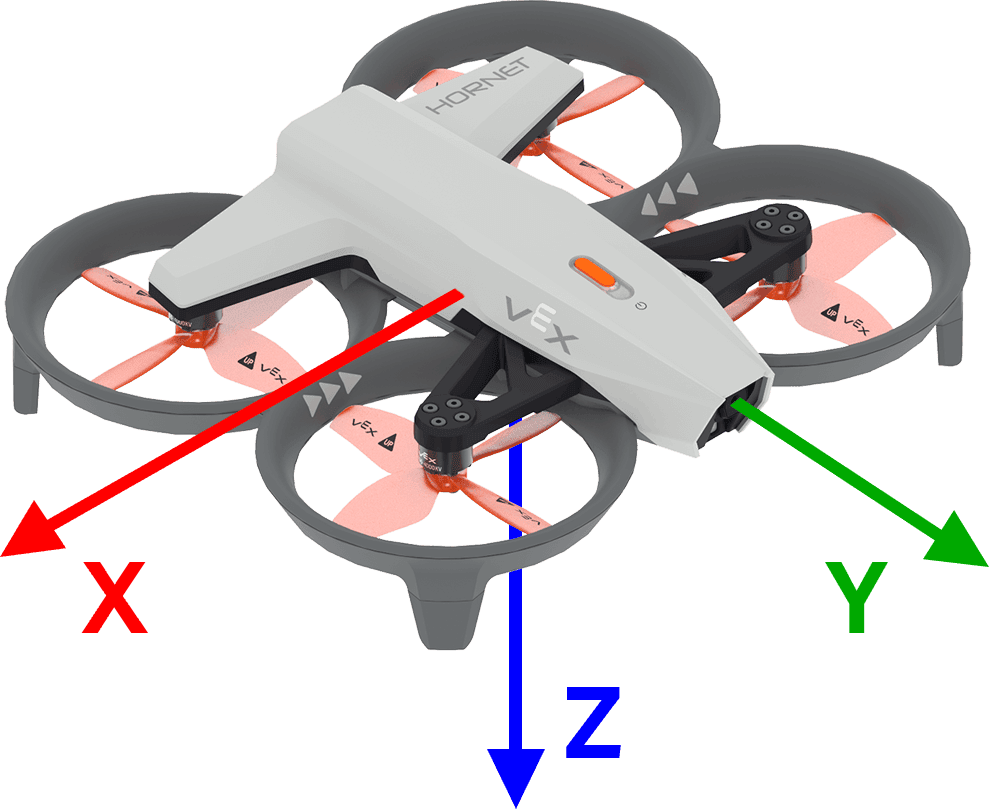
When describing drone movements:
- The z-axis represents the drone’s throttle. This is the up and down movement.
- The y-axis represents the drone’s pitch. This is the forward and backward movement.
- The x-axis represents the drone’s roll. This is the side-to-side movement. (You will learn about roll in Unit 4.)
Using the axes to describe flight paths helps pilots give precise instructions. For example, if a drone takes off, then flies forward through the first red ring, we can say that it moved up along the z-axis, then forward along the y-axis.
Understanding where each movement occurs on the axes gives you a clearer sense of how the drone navigates space and how pitch works with other controls like throttle.
Check Your Understanding
Select Next > to move to the next lesson.