You have created projects with repeating behaviors using Forever blocks previously, but what if you wanted to repeat behaviors for a finite number of times? In this lesson, you'll learn about the Repeat block, and how it can be used to repeat code a specific number of times. Then you'll apply what you learned to code your VEX AIM Coding Robot to react to four AprilTag IDs as well as four different cargo objects.
Watch the video below to learn about:
- How the Repeat block works in a project
- Why to use a Repeat block instead of a Forever block in a project
Now that you have watched the video, capture your thoughts in your journal. Answer these questions to guide your thinking and help you prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- Why is it useful to be able to easily repeat behaviors in a project?
- What evidence from the video supports your answer?
- Think about your previous projects – would a Repeat block have been useful? Why or why not?
- What questions do you have about coding with a Repeat block?
Now that you have watched the video, capture your thoughts in your journal. Answer these questions to guide your thinking and help you prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- Why is it useful to be able to easily repeat behaviors in a project?
- What evidence from the video supports your answer?
- Think about your previous projects – would a Repeat block have been useful? Why or why not?
- What questions do you have about coding with a Repeat block?
After students watch the video and before practicing, come together for a whole-class discussion. Use student answers to the questions provided as the basis for discussion.
As students discuss the difference between repeating code with a Repeat block and a Forever block, it is important to keep in mind that there is not one “right” answer when it comes to coding the robot to complete a task. Encourage students to think critically about the reasoning behind their coding choices. The Toolbox in VEXcode AIM is just that - a set of tools - and students should be encouraged to explore and test to find the right tool for the job at hand.
To learn more about the blocks in the Logic category of the Toolbox, view the VEXcode API Reference - Logic - Controls.
Guided Practice
Now that you have watched and discussed the video, it's your turn to practice!
Step 1: Set up the field. Use the image below as a guide. AprilTags can be randomly placed in the corners, and cargo objects (sports balls and barrels) can be randomly placed in the center of each wall.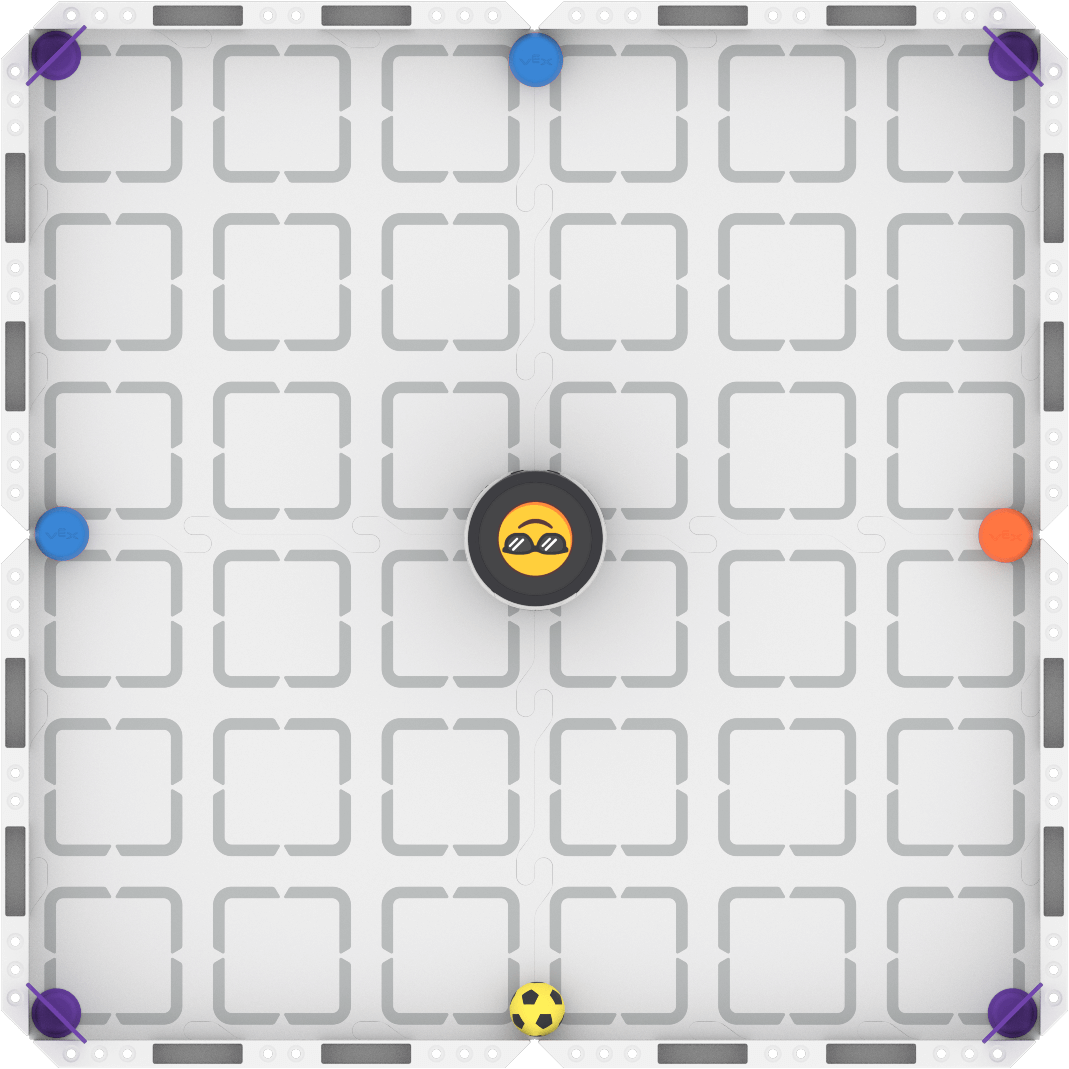
Step 2: Plan your project to make the robot react differently depending on the object or AprilTag ID detected. Together with your group, choose how you want your robot to react to each of the AprilTag IDs and objects on your field. Document your plan in your journal, and be specific.
- Use this task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to guide you as you complete the activity.
- Pro Tip: Look at the orientation of the cargo objects and the AprilTags in relation to one another. Use what you know about headings and angles to help you repeat turning movements effectively.
Step 3: Code your robot to complete the activity, making sure it reacts differently depending on the AprilTag ID or object detected. Continue to use your task card.
- Pro Tip: You can use your project from the previous lesson as the basis for this one. Be sure to adjust your comments to match the intent of this project.
Resources for Practice:
The articles linked here are available if you need additional support while completing the activity.
Now that you have watched and discussed the video, it's your turn to practice!
Step 1: Set up the field. Use the image below as a guide. AprilTags can be randomly placed in the corners, and cargo objects (sports balls and barrels) can be randomly placed in the center of each wall.
Step 2: Plan your project to make the robot react differently depending on the object or AprilTag ID detected. Together with your group, choose how you want your robot to react to each of the AprilTag IDs and objects on your field. Document your plan in your journal, and be specific.
- Use this task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to guide you as you complete the activity.
- Pro Tip: Look at the orientation of the cargo objects and the AprilTags in relation to one another. Use what you know about headings and angles to help you repeat turning movements effectively.
Step 3: Code your robot to complete the activity, making sure it reacts differently depending on the AprilTag ID or object detected. Continue to use your task card.
- Pro Tip: You can use your project from the previous lesson as the basis for this one. Be sure to adjust your comments to match the intent of this project.
Resources for Practice:
The articles linked here are available if you need additional support while completing the activity.
Remind students of shared expectations for collaborative coding and discussions before beginning.
Distribute the Lesson 2 task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to each student. Students will use the same task card for the whole activity. They should first plan their projects with their groups, then check in with you to share their plans before beginning to code. Remind students that they can use comments to incorporate their project plans directly into their VEXcode projects.
Students can use the project they created in the previous lesson as the basis for this one. If students are using an existing project, remind them to use the Save As option in the File menu of VEXcode, so that they keep both projects separate. Learn more about saving and opening projects in this article.
As students are building and testing their projects, circulate around the room and engage in discussions about their process and progress. Ask questions like:
- What behaviors have you coded so far? What is your next step?
- How are you using AI Vision in this project? What have you learned about AI Vision that is helping you to be successful here?
- What behaviors do you think you will need to repeat? How will you do that?
- How are you commenting your code to help you organize your project? Would your comments help someone else understand why the blocks are in your project? Why or why not?
If students are struggling with what to iterate on, encourage them to think creatively about the reactions they are coding. How can they apply things like custom images or actions to help make their reactions clearer or more expressive?
Wrap-Up
Now that you have practiced, it is time to share what you learned. Answer the following questions in your journal to help you reflect on your learning and prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- How would you explain the difference between a Repeat and a Forever block to someone new to our class?
- How did you repeat behaviors in your project? Explain your rationale for the blocks you chose.
- What was the most challenging part of this project for you? How did your group work together to solve the problem?
- How did your group collaborate to plan and code your project? What has helped your collaboration to improve since the start of the course?
Now that you have practiced, it is time to share what you learned. Answer the following questions in your journal to help you reflect on your learning and prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- How would you explain the difference between a Repeat and a Forever block to someone new to our class?
- How did you repeat behaviors in your project? Explain your rationale for the blocks you chose.
- What was the most challenging part of this project for you? How did your group work together to solve the problem?
- How did your group collaborate to plan and code your project? What has helped your collaboration to improve since the start of the course?
Guide students to share their learning in a whole-class discussion. Help students reflect on their learning through practice to converge on shared understandings or learning targets.
Use the questions students answered in their journals as the starting point for the discussion. Ask follow-up questions to guide student understanding:
- On repeating behaviors:
- Can you think of a previous project from the course where you would have made a different choice than you did here? Why?
- What are the advantages of using a loop to repeat code? Are there disadvantages? Why or why not?
- On challenges and collaboration:
- What resources have you used to help you figure something out or answer a question? What was the most helpful to you? Why?
- If you had a new partner, how would you apply what you've learned about collaborative coding to make you successful?
- What are some problem solving strategies that you've learned that help you overcome obstacles?
Select Next > to move on to the next lesson.