San Francisco and Seismic Isolators

Seismic isolation helps prevent major catastrophes!
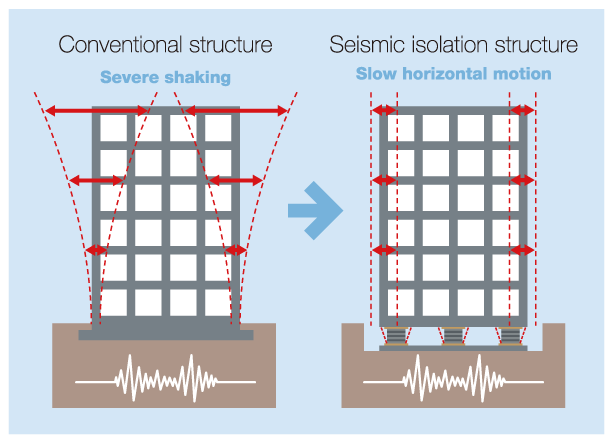
Conventional buildings are constructed with the foundation laid right into the ground. Buildings built this way will shake with the earth if an earthquake occurs there. This would cause extensive damage due to the severe shaking motion.
Seismic isolation (or base isolation) is when the building is built on top of pads or flexible bearings. When the building is built this way, the building structure is resting away from the ground. This allows the entire building to move in a slow horizontal motion during earthquakes. Reducing the shaking makes the building safer and sturdier in an earthquake.
Many cities in the world commonly have earthquakes, such as San Francisco. Builders there design buildings to use base isolators to make them safer. Even though this costs more money to do, the added safety is worth the cost.