Programming Loops - Python
The Clawbot V5 is ready to move!
This exploration will give you the tools to be able to start creating some cool projects that use loops.
- VEXcode V5 Python instructions that will be used in this exploration:
- drivetrain.drive_for(FORWARD, 300, MM)
- drivetrain.turn_for(RIGHT, 90, DEGREES)
- claw_motor.spin_for(REVERSE, 70, DEGREES)
- arm_motor.spin_for(FORWARD, 360, DEGREES)
- bumper_b.pressing()
- while True:
- for repeat_count in range(4):
- wait(5, SECONDS)
You can use the Help information inside of VEXcode V5 to learn about individual Python commands.
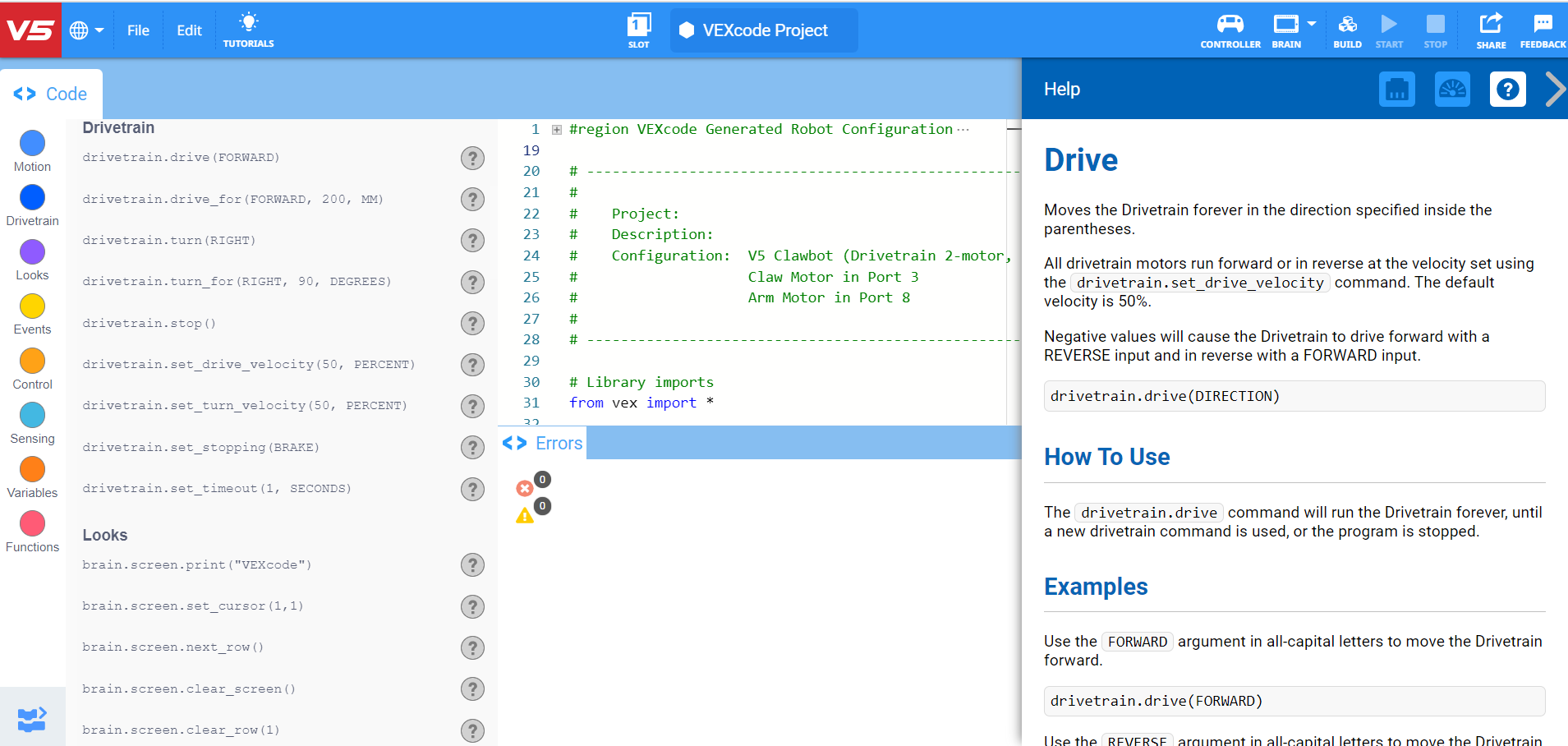
Make sure you have the hardware required, your engineering notebook, and VEXcode V5 downloaded and ready.
| Quantity | Materials Needed |
|---|---|
| 1 |
VEX V5 Classroom Starter Kit (with up-to-date firmware) |
| 1 |
VEXcode V5 (latest version, Windows, macOS) |
| 1 |
Engineering Notebook |
| 1 |
Clawbot Template (Drivetrain 2-motor, No Gyro) example project |
Step 1: Let's start programming with loops
- Before you begin your project, select the correct template project. The Clawbot Template (Drivetrain 2-motor, No Gyro) example project contains the Clawbot's motor configuration. If the template is not used, your robot will not run the project correctly.
-
Select File and Open Examples.
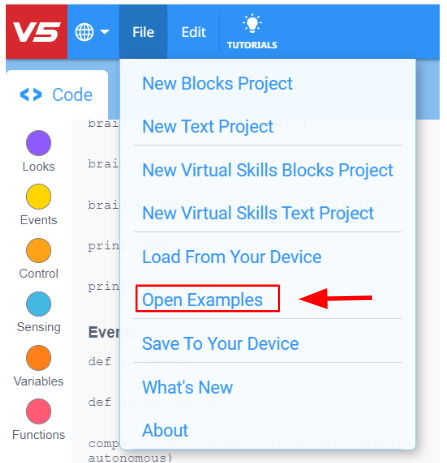
-
Scroll through the different Example projects. These projects demonstrate a variety of actions your Clawbot can perform. Select and open the Clawbot Template (Drivetrain 2-motor, No Gyro) example project.

-
Name the project RepeatingActions.
-
Type the following code:
# Library imports from vex import * # Begin project code # Drives forward 300mm turns 90 degrees for 4 iterations for repeat_count in range(4): drivetrain.drive_for(FORWARD, 300, MM) drivetrain.turn_for(RIGHT, 90, DEGREES) wait(5, SECONDS)
Look over the project and then do the following in your engineering notebook.
-
Predict what the project will have the Clawbot do. Explain more than the fact that the project repeats.
What is it repeating? What is the Clawbot doing?
- Write your prediction, but do not break the short project into more than two parts.
-
Save, download, and run the Repeating Actions project.
- Check your explanations of the project in your engineering notebook and add notes to correct them as needed.
Step 2: Run the project and observe the robot

Look at the Repeating Actions project (the second project) again. This project will repeat the forward and then turn behavior four times. A "repeat" loop structure (using a for loop) is used when you want to use a set of behaviors a certain number of times.
If the repeat structure is replaced with a while loop structure, the robot will repeat the forward and then turn behaviors "while" the condition is true. You can also set the condition to "true" to have the while loop continue forever.
In the first project, a sensor's input is used to determine when to begin turning. The project on the right uses a fixed Drivetrain distance to determine when to begin turning.
In order to continually check a sensor's input, an if else statement is used together a while loop. In the project on left, the robot will turn right when the "bumper_b" sensor is pressed, otherwise the robot will drive forward forever if the "bumper_b" sensor is not pressed. To continually check the bumper_b sensor's value, the if statement is within a while loop.
The first project is a practical use-case of a structure that repeats forever – using while loops and if statements together. Imagine a self-driving sweeper that continues to drive forward until it runs into a wall or object, then turns before continuing to drive.
Step 3: The Squared Loops Challenge!

- Have your Clawbot drive in a square.
- Before each turn, the claw must be opened and closed, and the arm must be raised and lowered.
- The Clawbot cannot drive along a side of the square more than once.
- You can use the RepeatingActions project from above as a starting point but save it as SquaredLoops before making any changes.
In your engineering notebook, plan the following:
- Plan out your solution and predict what each instruction in your project will have the Clawbot do.
- Download and run your project to test it before submitting it.
- Make changes to the project as needed and take notes about what was changed during testing.