In this lesson, you will explore how the VEX AIM Coding Robot “sees” its environment, by using the AI Vision Dashboard in VEXcode AIM. You'll also build on what you've learned about using macro blocks as you code the robot to deliver barrels to an AprilTag using the Move to object block.
Watch the video below to learn about:
- How the AI Vision Sensor perceives its environment
- How the AI Vision Dashboard in the Monitor tab of VEXcode AIM allows you to view sensor feedback in real time.
- How to code the robot to move to an AprilTag using the Move to object block.
Now that you have watched the video, capture your thoughts in your journal. Answer these questions to guide your thinking and help you prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- How do you envision using the AI Vision Dashboard to help you code your robot using the AI Vision Sensor?
- How do you think robot perception is different from human perception?
- How do you think the Move to object block will be useful?
- What evidence do you have from the video that supports your ideas?
- What are some questions you have after watching the video? What do you think will help you answer them?
Now that you have watched the video, capture your thoughts in your journal. Answer these questions to guide your thinking and help you prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- How do you envision using the AI Vision Dashboard to help you code your robot using the AI Vision Sensor?
- How do you think robot perception is different from human perception?
- How do you think the Move to object block will be useful?
- What evidence do you have from the video that supports your ideas?
- What are some questions you have after watching the video? What do you think will help you answer them?
After students watch the video and before practicing, come together for a whole-class discussion. Use student answers to the questions provided as the basis for discussion.
Exploring the difference between the way a robot or computer sees the world, and the way humans see the world helps students to develop fundamental understandings about how AI works. Humans get information about their environments through their five senses, whereas robots must use sensor feedback to do so. It is important to return students' attention to this exploration throughout this lesson and beyond so they can fully understand this key concept in AI.
Additionally, the term “field of view” is used to describe the area in which the AI Vision Sensor can perceive objects. Introduce and reinforce this term in conversation throughout this lesson.
Guided Practice
Now that you have watched and discussed the video, it is your turn to practice!
Step 1: Set up your field as shown in the image below.
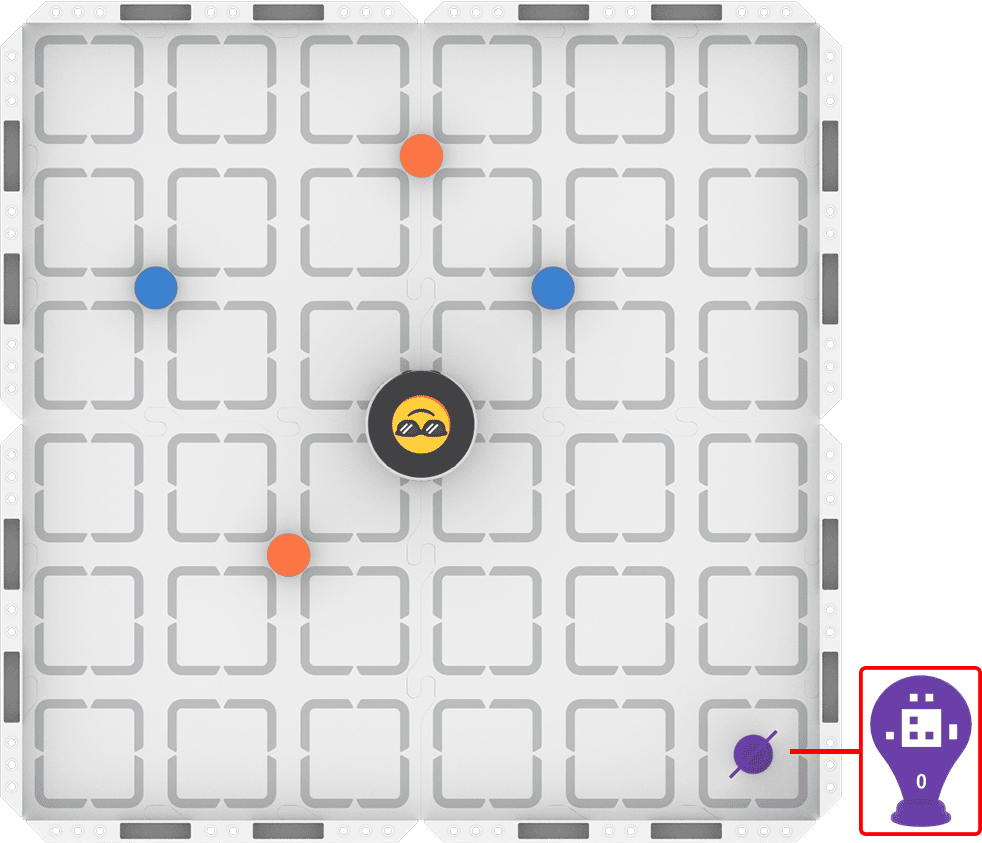
Step 2: Use Drive mode to model the movements your robot needs to make to complete the task.
- Your task is to drive the robot to pick up each of the four barrels and place them in front of AprilTag ID 0. Document your driving, then plan how to code that movement.
- Use this task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to guide your practice.
- Pro Tip: After you place each barrel in front of the AprilTag, remove it from the field by hand. This allows the AI Vision Sensor to have the AprilTag in its field of view.
Step 3: Code the robot to complete the task.
- Your task is to use your path plan from Step 2 to code the robot to pick up each of the four barrels and place them in front of AprilTag ID 0.
- Use this task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to guide your practice.
- Pro Tip: Use the AI Vision Dashboard in the Monitor tab to help you. To learn more about the AI Vision Dashboard, view this article.
Step 4: Explore! Move between driving and coding to iterate on your project and improve your strategy.
- Together with your group, brainstorm ways to make your project better.
- Drive the robot to test out your ideas, and choose one to start with.
- Iterate on your project to make it match the new driven behaviors.
- Continue to move between driving and coding frequently to iterate on your project and find the best strategy to complete the task!
Resources for Practice:
The articles linked here are available if you need additional support while completing the activity.
Now that you have watched and discussed the video, it is your turn to practice!
Step 1: Set up your field as shown in the image below.

Step 2: Use Drive mode to model the movements your robot needs to make to complete the task.
- Your task is to drive the robot to pick up each of the four barrels and place them in front of AprilTag ID 0. Document your driving, then plan how to code that movement.
- Use this task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to guide your practice.
- Pro Tip: After you place each barrel in front of the AprilTag, remove it from the field by hand. This allows the AI Vision Sensor to have the AprilTag in its field of view.
Step 3: Code the robot to complete the task.
- Your task is to use your path plan from Step 2 to code the robot to pick up each of the four barrels and place them in front of AprilTag ID 0.
- Use this task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to guide your practice.
- Pro Tip: Use the AI Vision Dashboard in the Monitor tab to help you. To learn more about the AI Vision Dashboard, view this article.
Step 4: Explore! Move between driving and coding to iterate on your project and improve your strategy.
- Together with your group, brainstorm ways to make your project better.
- Drive the robot to test out your ideas, and choose one to start with.
- Iterate on your project to make it match the new driven behaviors.
- Continue to move between driving and coding frequently to iterate on your project and find the best strategy to complete the task!
Resources for Practice:
The articles linked here are available if you need additional support while completing the activity.
Remind students of their established group work expectations before beginning.
Distribute the Step 2 task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to each student. Remind students that the goal of driving is to ensure everyone in the group develops a shared mental model of how the robot should move to complete the task successfully. Encourage students to be mindful of how they document their driving, as they will use their practice as documentation to build their code.
As students are driving, circulate around the room and check in with students about their learning. Ask questions like:
- When you drive using the AI Vision Sensor, what do you notice about how the robot moves to pick up each barrel?
- Have you observed anything unexpected while driving? If so, how might that observation affect your coding decisions?
- If your group is disagreeing about what to document, or what path to try first when coding, how are you resolving that?
Distribute the Step 3 task card (Google / .docx / .pdf) to each student after they have met the success criteria for driving, and shared their planned path with you. Students will then use their plan to build their initial VEXcode projects. Remind them to build and test their projects incrementally.
As students are coding the robot, circulate around the room and check in with students to discuss their progress and learning. Ask questions like:
- Are you using the AI Vision Dashboard to help you code? If so, how?
- How is coding this project different from driving? How is it similar?
- What ideas that you developed by driving have you applied to your coding project? Did they work as expected? Why or why not?
Once students have an initial coding project that completes the task, they should move on to Step 4 and begin iterating.
- What if you needed to adjust your robot’s speed or precision for this project? What strategies could help?
- What are you noticing about how robots perceive their environments? Does driving give you different insights than coding?
- How are you making collaborative decisions about what parts of your project to change? How are you agreeing on what change to make?
Wrap-Up
Now that you have practiced, it is time to share what you learned. Answer the following questions in your journal to help you reflect on your learning and prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- How has driving and coding the robot in this lesson helped you to understand how robots use sensors to perceive the world? Explain using evidence from your journal.
- In what situations do you think the Get object block would be most useful?
- What information did you learn from the AI Vision Dashboard in the Monitor tab, and how did it help you understand what the robot was doing?
- Have your collaboration strategies changed over this course? If so, explain how. If not, what would you like to improve?
Now that you have practiced, it is time to share what you learned. Answer the following questions in your journal to help you reflect on your learning and prepare for a whole-class discussion:
- How has driving and coding the robot in this lesson helped you to understand how robots use sensors to perceive the world? Explain using evidence from your journal.
- In what situations do you think the Get object block would be most useful?
- What information did you learn from the AI Vision Dashboard in the Monitor tab, and how did it help you understand what the robot was doing?
- Have your collaboration strategies changed over this course? If so, explain how. If not, what would you like to improve?
Guide students to share their learning in a whole-class discussion. Help students reflect on their learning through practice to converge on shared understandings or learning targets.
Use the questions students answered in their journals as the starting point for the discussion. Ask follow up questions to guide student understanding:
- On the AI Vision Sensor:
- What does the Dashboard tell you about the AI Vision Sensor? What does it not tell you? What other information would you like to have about the objects the AI Vision Sensor detects?
- How does the way the AI Vision Sensor perceives the world differ from the way your eyes see the world?
- Do you think your eyes are more or less powerful than the AI Vision Sensor? Why?
- On coding with macro blocks:
- What are all the behaviors that the robot completes in the course of executing a Move to object block, or any macro block?
- What data from the sensor do you think is being used in the macro block?
- On collaboration:
- How has your ability to solve problems collaboratively improved?
- What would you like to do better?
- What steps could you take towards that goal?
Return to the shared document you created during Lesson 1 that lists questions students have about the AI Vision Sensor. Update it with students' answers based on the new information they have learned during this lesson. Record any new questions that have arisen.
Select Next > to move on to the Unit Challenge.