Controllers and Loops - Blocks-based
Controllers and Loops
In competitions, teams must manipulate their robots wirelessly with controllers. The controller is programmed to update the robot based on input from the user. Loops are used in the project so that the robot repeatedly checks for updated input information. Loops allow the project to rapidly check which buttons have been pressed, or how far joysticks have been pushed. Once checked, this information is quickly relayed to the robot so that it responds quickly to the controller's instructions.
The following image shows the Tank Drive example project from VEXcode V5. The forever loop in this project checks the positions of Axes 2 and 3 forever in order to set the velocity of the motors.
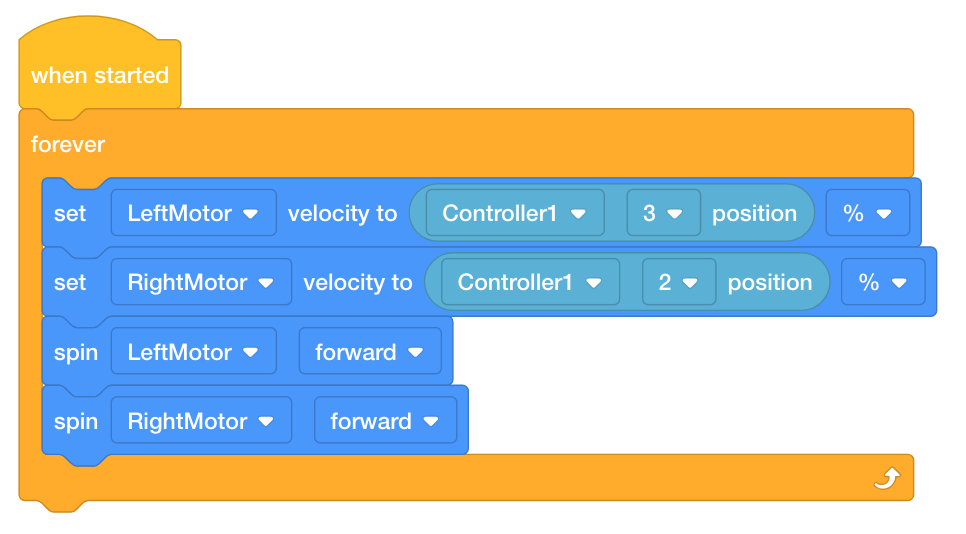
Loops are important even for autonomous programming without a controller. A loop helps to simplify and organize repeated commands within a project.
![]() Extend Your Learning
Extend Your Learning
To expand this activity, ask your students to explore the differences between arcade control and tank control. Students can follow the example projects found in VEXcode V5. There are four example projects: Left Arcade, Right Arcade, Split Arcade, and Tank Drive.


Discuss how the loops within the programs work, as well as the pros and cons of each type of control.
To relate this activity to math, use the left/right arcade (one joystick) and split arcade/tank drive (both joysticks) projects above to discuss the roles of the X and Y axes within the project.
Select "Next" to move on!