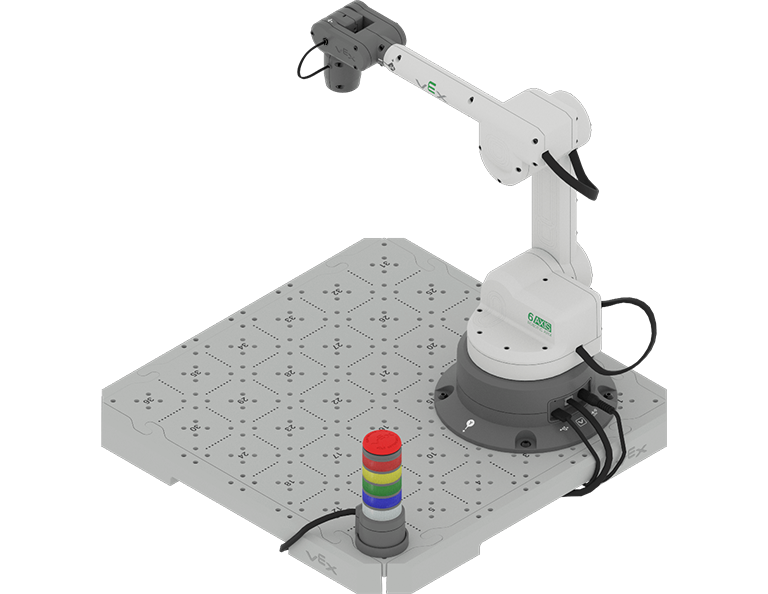
In this Course, you will be introduced to the world of industrial robots with the CTE Workcell Kit. You will learn about factory automation and the role of industrial robotics within it. You will be introduced to the CTE 6-Axis Robotic Arm and how to connect it to your computer, so you can begin to explore manual movements.
Watch the following introduction video for an overview of what you will learn in this Unit.
Setting Up Your Engineering Notebook
Throughout this course you will use an engineering notebook to document your notes, learning, projects, and reflections. In each Unit, you will be prompted to record information, learning targets, answers to Check Your Understanding questions, and more in your engineering notebook. It is important to use your notebook consistently, so you can go through it and use the information you recorded to help you with course activities, Wrap Up Reflections, and to ask and answer questions related to your learning targets.
Watch the video below to learn about setting up your engineering notebook, and how you can make your notebook unique to you.
Your Digital Engineering Notebook
You will need your own engineering notebook, which you will add to continuously throughout the course. The CTE Digital Engineering Notebook is available as Google Slides or Microsoft PowerPoint. If you are using the Google Slides version, you will be required to make a copy when the link is opened. Select Make a copy when prompted, as shown here.
- Make a copy of the CTE Digital Engineering Notebook Template. This will be your engineering notebook for the entire course. Select either the Google Slides link OR the Microsoft PowerPoint link below.
- Make a copy of the Digital CTE Parts. This slideshow will give you images that you can use to create custom pages in your digital engineering notebook to meet your needs throughout the course. Select either the Google Slides link OR the Microsoft PowerPoint link below.
- Make a copy of the instructions for how to use the CTE Digital Engineering Notebook. This slideshow will give you helpful information for using your notebook, as well as tips and tricks for making the most of your digital engineering notebook throughout the course. Select either the Google Slides link OR the Microsoft PowerPoint link below.
- Add your name to the file names of each of the CTE Digital Engineering Notebook files you just downloaded. Be sure that you can easily access your digital notebook on your device, as you will be using the same engineering notebook for the entire course.
Co-Create Learning Targets
Now that you have watched the video and know that you will be learning about factory automation and industrial robotics, you will begin by learning about 6-Axis Robotic Arm and how to connect it to your device. You will also learn about the coordinate system of the 6-Axis Arm and how to gather coordinates using manual movements. By the end of this Unit, you will be able to gather coordinates of specific locations on the CTE Tile with the 6-Axis Arm. It is time to think about what you will need to learn and know in order to accomplish those tasks.
You will co-create learning targets with your group and your teacher to capture these goals, so that you have a shared understanding of your learning goals for the Unit. You will write your learning targets in your engineering notebook so you can refer to them throughout the Unit.
It is helpful to phrase learning targets in the form of "I can" statements. Example learning targets for this Unit could include:
- I can identify the 6 axes on the 6-Axis Arm.
- I can connect the 6-Axis Arm to my computer.
- I can describe how the 6-Axis Arm moves along the x-axis.
- I can record the x, y, and z-coordinates of a location in my engineering notebook.
To create your learning targets, first brainstorm what you will need to know to be able to complete the activities shown in the video above. Make a list in your engineering notebook of what you will need to know, learn, and do, like this:
- Identify the 6 axes on the 6-Axis Arm.
- Connect the 6-Axis Arm to your device.
- Describe the movement of the 6-Axis Arm along the x, y, and z-axes.
- Gather x, y, and z-coordinates using the Teach Pendant.
- Use my engineering notebook to record the x, y, and z-coordinates of a specific position.
- Organize our group's work so we complete the activity collaboratively.
Next, co-create learning targets based on your list. Think about how each of the things you listed can be framed into a learning target, using "I can" statements. You can use this template to help you write your learning targets in your engineering notebook. (Google Doc / .docx / .pdf)
For example, the list item "Identify the 6 axes on the 6-Axis Arm" can be shifted to the learning target of "I can identify the 6 axes on the 6-Axis Arm."
The following table shows an example of how the Learning Target Organizer in your engineering notebook could be filled out.
| Learning Target Category | Learning Targets |
|---|---|
|
Knowledge Targets What do I need to know and understand in order to be successful in the Unit? |
|
|
Reasoning Targets What can I do with what I know and understand in order to be successful in the Unit? |
|
|
Skill Targets What can I demonstrate to show I understand the concepts and skills needed to be successful in the Unit? |
|
Share your learning targets with your teacher. Adjust them as needed so that you, your group, and your teacher are all in agreement.
Vocabulary
In this Unit, you will be introduced to concepts about industrial robotics, using elements of the CTE Workcell Kit, and VEXcode EXP. This vocabulary list is here to provide reference for any new terms you may come across. Record this vocabulary in your engineering notebook. Use this list as reference as you work through the Unit and encounter words you may not be familiar with.
- 6-Axis Robotic Arm
- A type of industrial robot with six points of rotation or movement, offering a wide range of motion and flexibility in tasks.
- Cartesian Coordinate System
- A grid-based system used to pinpoint locations in space using coordinates (x, y, z) to describe precise positions of points or objects.
- Industrial Automation
- Industrial automation is the use of technology and machines to streamline and improve manufacturing and production processes in factories, ensuring efficiency, consistency, and safety.
- Industrial Robots
- Automated machines capable of performing tasks in various industrial environments, often with more precision and endurance than human workers.
- Manual Movement
- The process of physically moving the 6-Axis Arm to gather coordinate data or perform specific tasks without automatic programming.
- Origin
- The location that all Cartesian coordinate values start from, (0,0,0).
- Teach Pendant
- A device used to manually control the actions of a robotic arm.
- Tool Center Point (TCP)
- The point at the end of a robot arm or tool used as a reference for movements and coordinates.
- Workcell
- An efficient arrangement of equipment and machinery designed to optimize production processes.
- VEXcode EXP
- The software used for coding and controlling the 6-Axis Arm.
| Quantity | Materials Needed |
|---|---|
| 1 per group | |
| 1 per group |
Computer |
| 1 per group |
VEXcode EXP |
| 1 per student |
Engineering Notebook |
Select Next > to learn more about industrial robotics.