Movement Challenge Preview
- 8 - 15 years old
- 45 minutes - 3 hours
- Intermediate
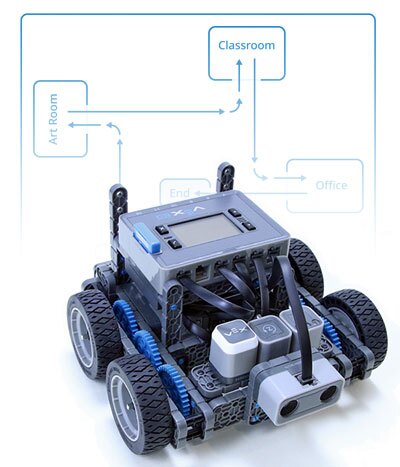
Description
Students will program their Autopilot to drive on a designated path through a sequence of movements.
Key Concepts
- Robot Behaviors
- Decompose the steps needed to solve a challenge
- Spatial Reasoning
- How to create, download and run a project
- Programming a sequence of movements
- How to save a project
Objectives
-
Build an Autopilot robot and configure the Smart sensors
-
Decompose problems into smaller subproblems to facilitate the program development process
-
Program the Autopilot to follow a specific path
-
Compare and refine algorithms for the same task and determine which is the most appropriate
-
Use operator blocks to make the robot move a precise distance
-
Test and debug a program to make sure it runs accurately
-
Describe choices made during program development using comments and presentations
Materials needed
-
Autopilot Robot
-
Charged Robot Battery
-
VEXcode IQ
-
USB Cable (if using a computer)
-
Engineering Notebook/ Graph Paper
-
Larger Paper
-
Rulers
-
Markers
-
Blocks (2-3 per group)
Facilitation Notes
-
Teacher support, discussion questions, tips, and student assessment are all organized in the STEM lab to give the teacher a successful engagement.
-
VEXcode IQ and VEXos Utility should be downloaded to each student device that will be used for programming the Autopilot.
-
Students should become familiar with the pieces before beginning to build the Autopilot. Each Superkit contains a poster containing true size representations of all the pieces contained in the kit.
-
Batteries should be charged prior to the start of the STEM lab.
-
An engineering notebook can be as simple as lined paper within a folder or binder. The notebook shown is a more sophisticated example that is available through VEX.
Further Your Learning
Educational Standards
Standards for Technological Literacy (STL)
-
Grades 3-5
-
1.D
-
2.H
-
9.C
-
9.D
-
10.C
-
11.F
-
11.G
-
12.D
-
12.G
-
-
Middle School
-
2.M
-
2.N
-
2.P
-
2.R
-
3.F
-
8.E
-
8.G
-
9.F
-
9.G
-
9.H
-
Computer Science Teachers Association (CSTA)
-
Grades 3-5
-
1B-CS-03
-
1B-AP-08
-
1B-AP-10
-
1B-AP-11
-
1B-AP-16
-
-
Grades 6-8
-
2-AP-15
-
2-AP-17
-
2-AP-18
-
Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
-
Grade 3-5
-
3-5 ETS 1-1
-
3-5 ETS 1-2
-
-
Middle School
-
MS-ETS1-1
-
MS-ETS1-1
-
MS-ETS1-3
-
MS-ETS1-4
-
Common Core State Standards - English and Language Arts (CCSS)
-
Grades 3-5
-
SL.3-5.1
-
W.3-5.2
-
RI.4.7
-
-
Middle School
-
RI.6.7
-
SL.6-7.4
-
SL.6-8.1
-
WHST.6-8.2
-
WHST.6-8.4
-
RST.6-8.3
-
7.RP.A.2
-
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
-
10.7.b.1
-
110.7.b.3
-
110.7.b.4
-
110.7.b.4
-
110.7.b.4
-
126.16.c.2
-
110.24.b.1
-
110.24.b.10
-
110.24.b.3
-
111.27.b.4
Florida State Standards (CPALMS)
-
LAFS.3-5.SL.1.1
-
LAFS.5.W.1.2
-
LAFS.4.RI.3.7
-
LAFS.68.WHST.1.2
-
LAFS.68.WHST.2.4
-
LAFS.68.RST.1.3
-
MAFS.7.RP.1.2
-
MAFS.K12.MP.1
-
MAFS.K12.MP.2
Indiana Academic Standards (IAS)
-
5.SL.2.1
-
5.W.3.2
-
5.ML.1
-
6-8.LST.5.2
-
6-8.LST.2.3
-
6.NS.8
-
PS.1
-
PS.2
Australian Standards